Understanding gross income is crucial for managing personal finances and running a successful business. This guide provides a clear breakdown of how to calculate gross income accurately, whether you’re an individual or a business owner.
What is Gross Income?
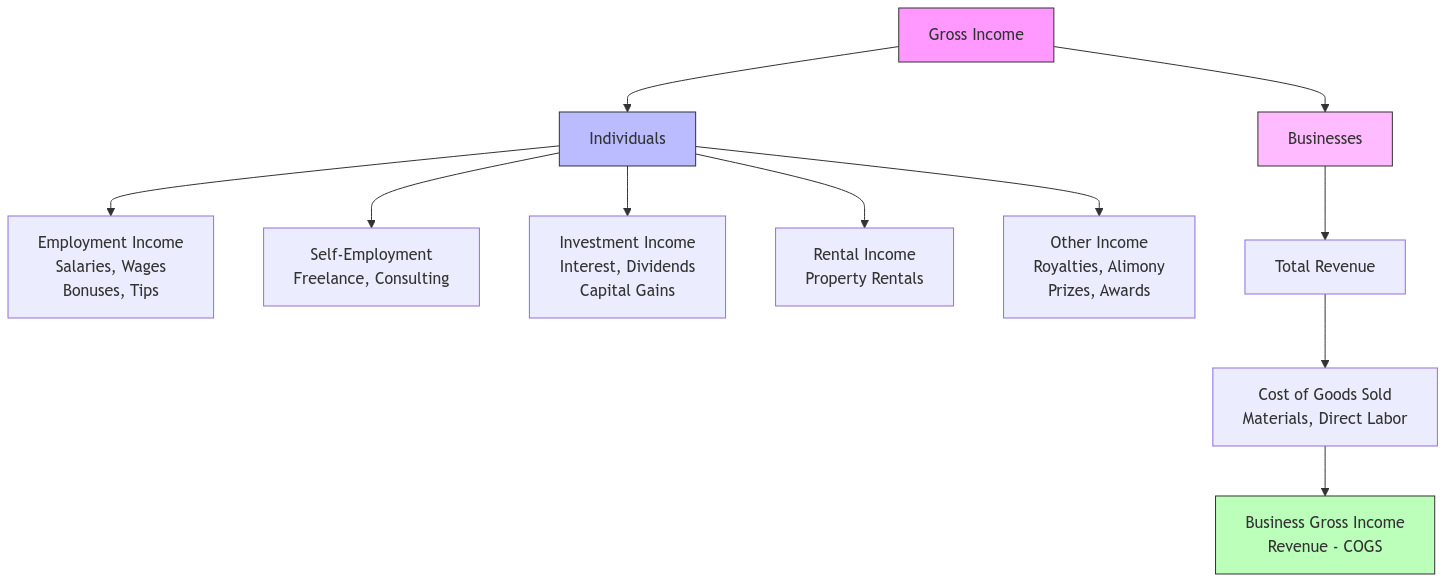
- For Individuals: Gross income is your total earnings before any deductions. It’s the top-line number on your paycheck before taxes, retirement contributions, and other withholdings. This includes wages, salary, bonuses, interest, dividends, rental income, and more.
- For Businesses: Gross income, often called gross profit, represents the revenue remaining after deducting the direct costs of producing goods or services (COGS). It reflects the profitability of a company’s core operations.
Why is Gross Income Important?
Knowing your gross income is essential for:
- Budgeting: Create a realistic budget and track spending effectively.
- Loan Applications: Lenders assess your ability to repay a loan based on your gross income.
- Rental Applications: Landlords use gross income to determine affordability.
- Tax Calculations: Gross income is the starting point for calculating your tax liability.
- Salary Negotiations: Provides a benchmark for salary discussions.
- Credit Limits: Credit card companies use gross income to set credit limits.
- Business Performance Analysis: Offers insights into product profitability and operational efficiency.
Calculating Gross Income
| Entity | Formula | Key Components |
|---|---|---|
| Individuals | Gross Income = All Income Sources – Certain Deductions | Salary, wages, tips, bonuses, interest, dividends, rental income, alimony received (for divorce decrees finalized before 2019), capital gains (sometimes) |
| Businesses | Gross Income = Total Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold | Sales revenue, service fees, other operating income. Cost of goods sold includes direct costs like materials and labor. |
Components of Gross Income: A Detailed Look
| Category | Individuals | Businesses |
|---|---|---|
| Employment Income | Salaries, wages, bonuses, commissions, tips | Not applicable (this is income for individuals employed by the business) |
| Self-Employment Income | Income from freelance work, consulting, sole proprietorships | Revenue from services provided, goods sold, or other business activities |
| Investment Income | Interest from savings accounts, dividends from stocks, capital gains from selling assets | Interest on business deposits, dividends from company stock holdings, capital gains from the sale of business assets |
| Rental Income | Income received from renting out property | Income from leasing out commercial property, equipment, or other assets |
| Royalties | Payments received for the use of intellectual property, such as books, music, or inventions | Income from licensing patents, trademarks, copyrights, or franchising agreements |
| Other Income | Alimony received, gambling winnings, lottery winnings, jury duty pay, prizes and awards | Income from lawsuits, government subsidies, insurance claims, non-operating income |
Understanding Capital Gains
Capital gains are the profits you make from selling an asset like stocks, bonds, or real estate. These are generally included in your gross income, but the tax rate can vary depending on how long you held the asset.
Gross Income vs. Net Income
- Gross Income: Total income before any deductions.
- Net Income: “Take-home” income after taxes and other deductions.
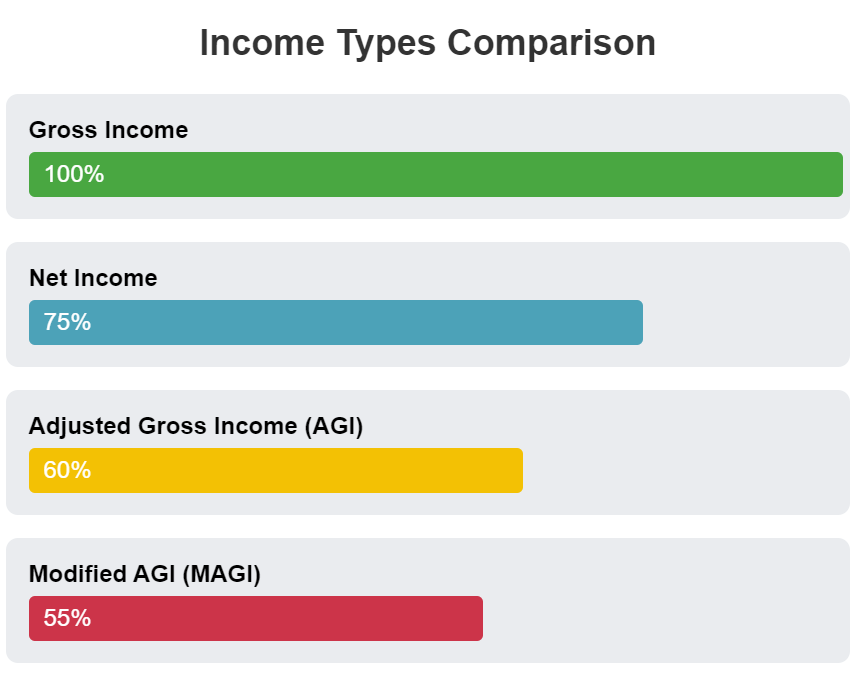
Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) and Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI)
- AGI: Calculated by subtracting certain above-the-line deductions from your gross income (e.g., contributions to traditional IRAs, student loan interest). AGI is used to determine eligibility for various tax benefits and credits.
- MAGI: A further refinement of AGI used to determine eligibility for specific tax benefits (e.g., Roth IRA contributions, Premium Tax Credit).
Recordkeeping Best Practices
- Maintain organized records of all income sources and deductible expenses.
- Keep pay stubs, bank statements, investment records, and business receipts.
- Use personal finance software or spreadsheets to track income and expenses.
Annual Recordkeeping Timeline
• Investment statements
• Mortgage interest statements
• Previous year’s tax returns
• Bank statements
• Tax filing receipts
• Payment confirmations
• Investment updates
• Business expense logs
• Q2 documents
• Property tax records
• Insurance documents
• Asset purchase records
• Charitable donations
• Year-end statements
• Tax planning documents
When to Consult a Professional
- Complex financial situations (multiple income sources, investments, business ownership)
- Significant life changes (marriage, divorce, job change)
- Uncertainty about deductions or credits
- Tax planning and preparation
FAQs
What’s the difference between gross income and net income?
Gross income is your total earnings before any deductions, while net income is what you actually take home after taxes, insurance, retirement contributions, and other deductions.
Do I need to include investment income in my gross income?
Yes, investment income such as interest, dividends, and capital gains should be included in your gross income calculations.
How do businesses calculate their gross income?
Businesses calculate gross income by subtracting the Cost of Goods Sold (COGS) from their total revenue. COGS includes direct costs like materials and labor used to produce goods or services.
Why is gross income important for loan applications?
Lenders use gross income to assess your ability to repay loans and determine how much you can borrow. It’s typically used to calculate your debt-to-income ratio, a key factor in loan approval.
Is rental income considered part of gross income?
Yes, any income received from renting out property should be included in your gross income calculations.
How does gross income affect my tax bracket?
Your gross income, after certain adjustments (becoming AGI), helps determine your tax bracket and overall tax liability. However, you’re typically taxed based on your taxable income, which is calculated after further deductions and exemptions.
What’s the difference between AGI and MAGI?
Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) is your gross income minus specific deductions like student loan interest. Modified Adjusted Gross Income (MAGI) adds back certain deductions and is used to determine eligibility for various tax benefits.
Should self-employed individuals calculate gross income differently?
Self-employed individuals should include all business revenue as gross income, but they can deduct business expenses to calculate their net profit, which becomes part of their personal gross income.
Connect with XOA TAX
Understanding your gross income is a crucial first step in navigating your financial landscape. If you’re facing complex tax situations or need personalized advice, don’t hesitate to contact the experts at XOA TAX. We’re here to help you with all your tax planning and preparation needs.
Website: https://www.xoatax.com/
Phone: +1 (714) 594-6986
Email: [email protected]
Contact Page: https://www.xoatax.com/contact-us/
Disclaimer: This post is for informational purposes only and does not provide legal, tax, or financial advice. Laws, regulations, and tax rates can change often and vary significantly by state and locality. This communication is not intended to be a solicitation, and XOA TAX does not provide legal advice. XOA TAX does not assume any obligation to update or revise the information to reflect changes in laws, regulations, or other factors. For further guidance, refer to IRS Circular 230. Please consult a professional advisor for advice specific to your situation.




 anywhere
anywhere  anytime
anytime