Living abroad as a US citizen or resident alien doesn’t exempt you from your US tax obligations. Your worldwide income is still subject to US taxation, even if you’re paying taxes in your country of residence. This can be a complex landscape to navigate, so we’ve created this guide to help you understand the essentials and fulfill your US tax duties while living overseas.
Key Concepts
- Foreign Earned Income Exclusion (FEIE): This valuable exclusion allows you to shield a portion of your foreign earned income from US taxation. For 2024, the FEIE limit is $126,500. To qualify, you must meet one of two tests:
- Physical Presence Test: You’ve been physically present in a foreign country or countries for at least 330 full days during a 12-month period.
- Bona Fide Residence Test: You’ve been a bona fide resident of a foreign country for an uninterrupted period that includes an entire tax year.
- Foreign Tax Credit: If you’ve paid taxes to a foreign government on your foreign income, you can potentially claim a credit against your US tax liability. This mechanism helps prevent double taxation.
- Tax Treaties: The US has established tax treaties with numerous countries to mitigate double taxation and offer other advantages to taxpayers. While these treaties can be beneficial, it’s important to remember that US citizenship-based taxation generally takes precedence.

Filing US Taxes from Overseas
- Gather Your Tax Documents: Ensure you have all necessary documents, including your Social Security number, W-2 forms (if applicable), and any other relevant tax forms.
- Choose a Filing Method: You have several options for filing: electronically using tax software, through a professional tax preparer, or by mail.
- File by the Deadline: The deadline for filing US taxes from overseas is typically April 15th. However, expats automatically receive an extension to June 15th. Important note: Even with the extension, any tax owed is still due on April 15th to avoid penalties.
- Consider Professional Help: If your tax situation is complex, seeking guidance from a qualified tax professional specializing in expat taxes is highly recommended.
Common Questions
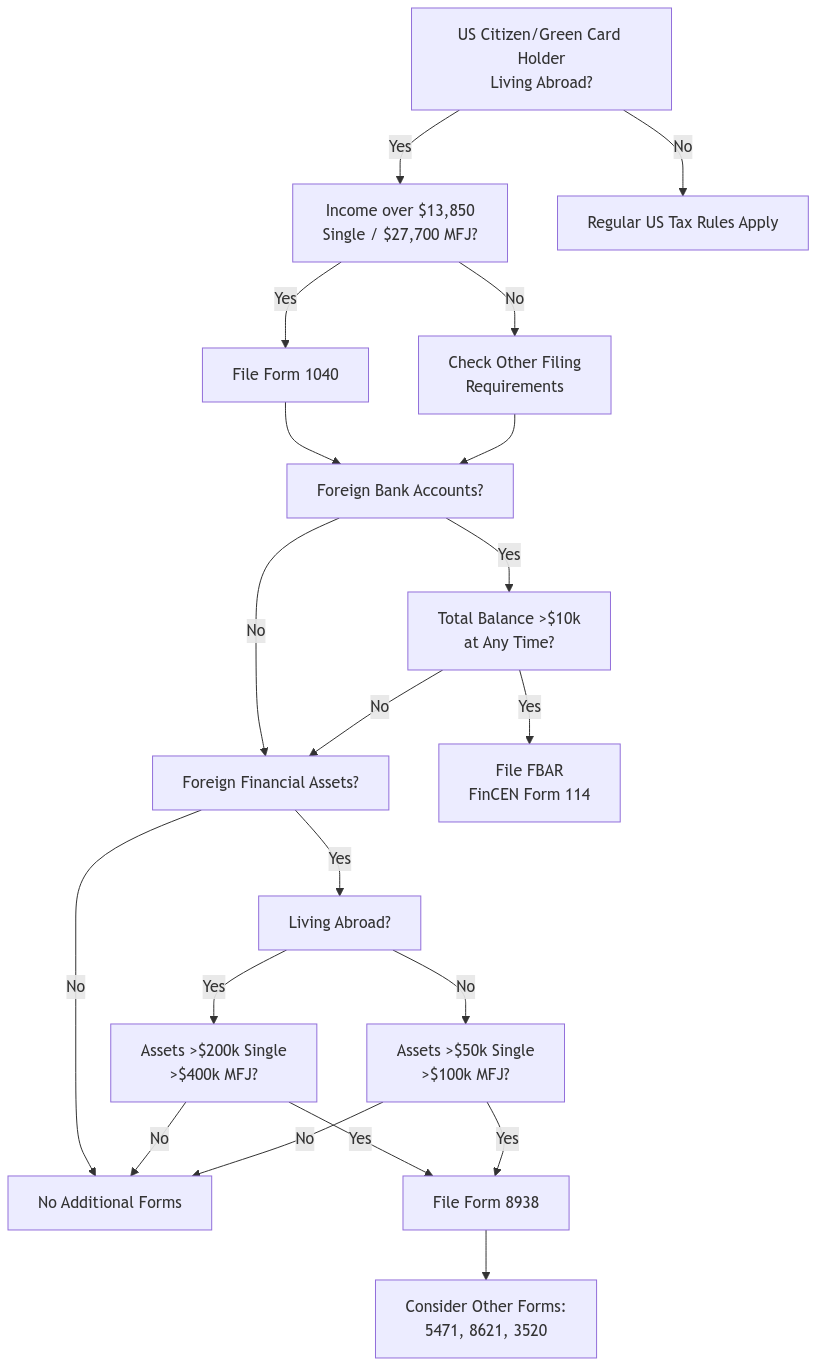
Bank Accounts: If you have foreign bank accounts with an aggregate balance exceeding $10,000 at any time during the year, you’re required to report them through the Foreign Bank Account Report (FBAR).
Investments: Your foreign investments may be subject to US taxes, including capital gains tax and dividend tax.
Retirement Plans: While contributions to some foreign retirement plans may be eligible for a tax deduction or exclusion in the US, this is not always the case. The specifics depend on the type of plan and your individual circumstances.
Additional Considerations for Expats
Self-Employment Tax: If you’re self-employed overseas, you’ll still be liable for US self-employment tax. Unfortunately, the FEIE doesn’t apply to this tax.
Housing Exclusion: In addition to the FEIE, you may also qualify for a housing exclusion, which can further reduce your taxable income.
FATCA Reporting: The Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA) requires US citizens to report certain foreign financial assets to the IRS. This is done by filing Form 8938 with your tax return if the total value of your specified foreign financial assets exceeds certain thresholds, which vary based on your filing status and whether you live in the US or abroad.
State Tax Obligations: Depending on your domicile and the laws of your state, you might still have state tax obligations even while living abroad.
FATCA Reporting: The Foreign Account Tax Compliance Act (FATCA) requires US citizens to report certain foreign financial assets to the IRS. This is done by filing Form 8938 with your tax return if the total value of your specified foreign financial assets exceeds certain thresholds. These thresholds vary based on your filing status and whether you live in the US or abroad:
| Filing Status | Threshold if Living in the US | Threshold if Living Abroad |
|---|---|---|
| Single | $50,000 | $200,000 |
| Married Filing Separately | $50,000 | $200,000 |
| Married Filing Jointly | $100,000 | $400,000 |
| Head of Household | $75,000 | $300,000 |
FAQs
Can I still contribute to my IRA while living abroad?
Yes, you can generally contribute to your IRA even while living abroad, as long as you have earned income. However, your ability to deduct traditional IRA contributions may be limited if you’re also claiming the Foreign Earned Income Exclusion.
Where can I find more information about tax treaties?
The IRS website has a dedicated section on tax treaties, where you can find detailed information about specific treaties and their provisions.
How does the Foreign Housing Exclusion work?
The Foreign Housing Exclusion is a valuable benefit that allows you to exclude qualifying housing expenses from your taxable income. The base amount for 2024 is 16% of the FEIE ($20,240), and the maximum exclusion varies by location, with higher limits in more expensive cities. Qualifying expenses include rent, utilities, insurance, and parking, but not property purchases, domestic help, or furniture. You must qualify for the FEIE to claim this exclusion. The amount you can exclude is the difference between your actual qualifying housing expenses and the base amount, up to the limit for your location.
What qualifies as foreign earned income?
Foreign earned income encompasses wages and salaries from foreign employers, self-employment income earned abroad, professional fees, and various allowances including housing and cost of living adjustments. However, it’s important to note that certain types of income don’t qualify, such as investment income, pension payments, Social Security benefits, and income earned while working for the US government or in international waters. The source of your income and where you perform the work are key factors in determining whether income qualifies as foreign earned.
How do totalization agreements affect self-employment tax?
Totalization agreements between the US and over 30 countries can significantly impact your self-employment tax obligations. These agreements help prevent double taxation of Social Security taxes and determine which country’s social security system you should contribute to. If you’re covered by a totalization agreement, you may be exempt from US Social Security taxes, but you’ll need proper certification from the foreign country. These agreements can affect your future benefits eligibility, so it’s important to understand the specific provisions of the agreement with your country of residence.
Website: https://www.xoatax.com/
Phone: +1 (714) 594-6986
Email: [email protected]
Contact Page: https://www.xoatax.com/contact-us/
Disclaimer: This post is for informational purposes only and does not provide legal, tax, or financial advice. Laws, regulations, and tax rates can change often and vary significantly by state and locality. This communication is not intended to be a solicitation, and XOA TAX does not provide legal advice. XOA TAX does not assume any obligation to update or revise the information to reflect changes in laws, regulations, or other factors. For further guidance, refer to IRS Circular 230. Please consult a professional advisor for advice specific to your situation.
