Tax season can feel overwhelming, but understanding your W-2 is crucial for a smooth filing experience. This guide breaks down everything you need to know about Form W-2, from how to read it to what to do if there are errors. Get expert tax tips and maximize your refund with XOA Tax.
Key Takeaways
- Your W-2 reports your annual wages and taxes withheld.
- Employers must send W-2s by January 31st.
- Use your W-2 to file federal and state tax returns accurately.
- Utilize the IRS “Where’s My W-2?” tool before contacting your employer or the IRS if you don’t receive your W-2 by mid-February.
What is Form W-2?
Form W-2, officially the “Wage and Tax Statement,” is a crucial document for filing your taxes. It summarizes your earnings and the taxes withheld from your paychecks during the year. You’ll receive a W-2 from each employer who paid you $600 or more in wages.
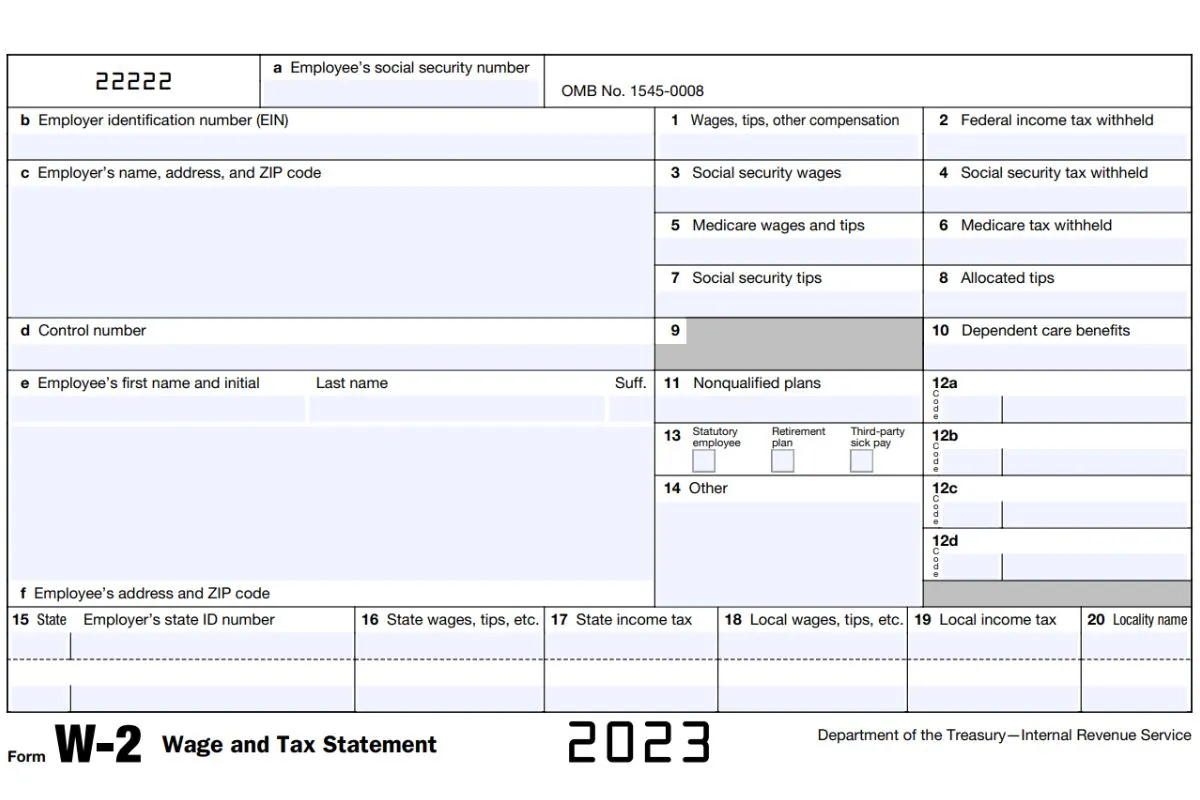
Your W-2 includes various types of income and deductions, which are essential for accurately calculating your tax liability. Understanding each section of the W-2 can help you ensure that your tax return is correct and that you maximize your refund.
Who Needs a W-2?
Employees receive W-2s. If you’re an independent contractor or freelancer, you’ll receive a 1099 form instead. Learn the difference between W-2 and 1099 forms.
The information on your W-2 is essential for accurately calculating your tax liability. If too much tax was withheld, you’ll get a refund. If not enough was withheld, you might owe taxes. Additionally, certain benefits and contributions reported on your W-2 can impact your overall financial picture.
How to Get Your W-2
If you haven’t received your W-2 by mid-February, follow these steps:
- Use the IRS “Where’s My W-2?” online tool to check the status of your W-2.
- If the tool indicates that your W-2 has been sent, verify your mailing address with your employer and request a copy if necessary.
- If you still haven’t received it by the end of February, contact your employer to request a copy and verify your mailing address.
- If your employer cannot provide the W-2, contact the IRS at 800-829-1040 for assistance in obtaining your W-2.
If you need to file your taxes before receiving your W-2, you might need to file for an extension or estimate your income and withholdings. Learn more about Form 1040 and filing your tax return.
How to Read Your W-2

Understanding your W-2 is easier than it looks. Here’s a breakdown of the key boxes:
| Box | Description |
|---|---|
| A | Your Social Security Number (SSN) |
| B | Your employer’s Employer Identification Number (EIN) |
| C | Employer’s name, address, and ZIP code |
| 1 | Wages, tips, other compensation |
| 2 | Federal income tax withheld |
| 3 | Social Security wages |
| 4 | Social Security tax withheld |
| 5 | Medicare wages and tips |
| 6 | Medicare tax withheld |
| 12 | Other income or deductions (e.g., 401(k) contributions, health insurance) |
| 17 | State income tax withheld |
| 20 | Local income tax withheld |
Each box on the W-2 serves a specific purpose. For example, Box 12 includes various codes that represent different types of compensation or benefits, such as retirement plan contributions (Code D) or health savings account (HSA) contributions (Code W). Understanding these codes can help you accurately report your income and deductions.
Refer to the official IRS W-2 instructions for a detailed explanation of all boxes.
Common W-2 Errors and How to Avoid Them
Mistakes on your W-2 can lead to delays in processing your tax return or trigger an IRS audit. Here are some common errors and how to avoid them:
- Incorrect Personal Information: Ensure your name, address, and SSN are correct. Verify this information with your employer.
- Wrong Earnings or Withholdings: Compare the amounts on your W-2 with your pay stubs. Report any discrepancies to your employer immediately.
- Missing Boxes: All relevant boxes should be filled out. If a box is missing that should be included, contact your employer for a corrected W-2.
- Incorrect Employer Information: Double-check your employer’s EIN and address. Errors here can cause issues with IRS processing.
To avoid these errors, regularly review your pay stubs and ensure that your employer has accurate records. Promptly addressing any discrepancies can save you time and prevent potential issues with your tax return.
Implications of Incorrect W-2 Information
Providing incorrect information on your W-2 can have several consequences:
- Delayed Refunds: Errors can cause delays in processing your tax return, delaying your refund.
- Additional Taxes Owed: Incorrect earnings or withholding amounts may result in owing more taxes than expected.
- IRS Audits: Significant discrepancies can trigger an audit, leading to more scrutiny of your financial records.
Ensuring the accuracy of your W-2 is essential to avoid these potential issues. Always double-check the information and seek professional assistance if you’re unsure about any details.
Strategies for Maximizing Your Refund
Beyond accurately using your W-2, here are some strategies to maximize your tax refund:
- Claim All Eligible Deductions and Credits: Ensure you’re taking advantage of all available tax deductions and credits, such as the Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC) or education credits.
- Contribute to Retirement Accounts: Contributions to 401(k)s or IRAs can reduce your taxable income.
- Adjust Withholdings: Review and adjust your W-4 to better match your tax liability, potentially increasing your take-home pay or optimizing your refund.
- File Electronically and Choose Direct Deposit: E-filing and direct deposit can speed up your refund process.
Working with a tax professional, like the experts at XOA Tax, can help you identify additional opportunities to maximize your refund and ensure your tax return is optimized for your financial situation.
What to Do if Your W-2 is Incorrect
If you spot any errors on your W-2, such as incorrect amounts, misspelled names, or wrong addresses, take the following steps:
- **Notify Your Employer:** Contact your employer immediately to request a corrected W-2 (Form W-2c).
- **Verify Information:** Double-check the corrected information to ensure all errors have been addressed.
- **File an Amended Return if Necessary:** If you’ve already filed your tax return with incorrect information, you may need to file an amended return using Form 1040-X.
Accurate W-2 information is essential to avoid processing delays or an IRS audit. If you need help correcting W-2 errors or have other tax questions, contact our team of tax experts at XOA Tax.
Frequently Asked Questions
What’s the difference between a W-2 and a W-4?
A W-4 is a form you fill out when you start a new job to indicate your tax withholding preferences. It tells your employer how much federal income tax to withhold from your paycheck. For example, if you claim more allowances on your W-4, less tax is withheld, increasing your take-home pay but potentially reducing your refund.
A W-2, on the other hand, is provided by your employer at the end of the year and summarizes your total earnings and the taxes withheld. You use the W-2 to file your tax return.
What if I don’t receive my W-2?
First, contact your employer to request a copy and verify your mailing address. If your employer cannot provide the W-2, use the IRS “Where’s My W-2?” tool to check its status. If you still don’t receive it by the end of February, contact the IRS at 800-829-1040. You can also use Form 4852 as a substitute for a missing W-2 when filing your tax return.
What’s the difference between a W-2 and a 1099?
A W-2 is for employees, detailing wages and taxes withheld by an employer. For example, if you work as a full-time employee at a company, you’ll receive a W-2.
A 1099 is for independent contractors or freelancers, reporting income earned without tax withholdings. For instance, if you work as a freelance graphic designer, your clients will issue you a 1099-NEC instead of a W-2.
This distinction affects how you file your taxes and pay self-employment taxes. Learn more.
Different Types of Income Reported on the W-2
Form W-2 not only reports your regular wages but also various types of compensation and benefits. Understanding these can help you accurately report your income and take advantage of available deductions.
- Box 12 Codes: These codes represent different types of compensation or benefits, such as:
-
- Code D: Elective deferrals to a 401(k) plan.
- Code W: Employer contributions to a Health Savings Account (HSA).
- Code DD: Cost of employer-sponsored health coverage.
-
- Box 14: This box may include additional information such as union dues, educational assistance payments, or other taxable benefits.
- Non-Taxable Benefits: Certain benefits, like employer-provided transportation or meals, may be non-taxable and are reported differently.
Properly categorizing and understanding these different types of income and benefits can help ensure your tax return is accurate and that you’re maximizing any potential deductions or credits.
Get Expert Tax Help from XOA Tax
Navigating tax season can be complex. Let our experienced team at XOA Tax handle your tax preparation and ensure you get the maximum refund you deserve. Contact us today for a stress-free tax experience.
Call us: (714) 594-6986
Email us: [email protected]
Contact Us




 anywhere
anywhere  anytime
anytime