Understanding Bookkeeping: The Backbone of Financial Management
Bookkeeping is essential for any business, providing a clear and organized method for recording financial transactions. At its core, it’s all about documenting the flow of money in and out of your business. These transactions are meticulously recorded following the company’s specific accounting guidelines and backed by actual documents. Common forms of these documents include:
- Bills and Receipts: Evidence of payments made or received.
- Invoices: Requests for payment for services or goods provided.
- Purchase Orders: Documents confirming purchase transactions.
Traditionally, these financial transactions could be logged manually in journals or spreadsheets. However, with advancements in technology, many businesses now leverage bookkeeping software like QuickBooks or Xero to streamline this process, offering more efficiency and reducing the room for error.
Bookkeeping is crucial for maintaining accurate financial records. By keeping your books in order, you gain a detailed picture of your company’s financial health, which is vital for making informed decisions, ensuring compliance, and optimizing growth potential. It sets the groundwork for profit maximization and sustainable business success.
Bookkeeping vs. Accounting: What’s the Difference?
 At first glance, bookkeeping and accounting may seem interchangeable. While they are often confused, they serve distinct roles in managing a business’s finances.
At first glance, bookkeeping and accounting may seem interchangeable. While they are often confused, they serve distinct roles in managing a business’s finances.
Bookkeeping: The Foundation
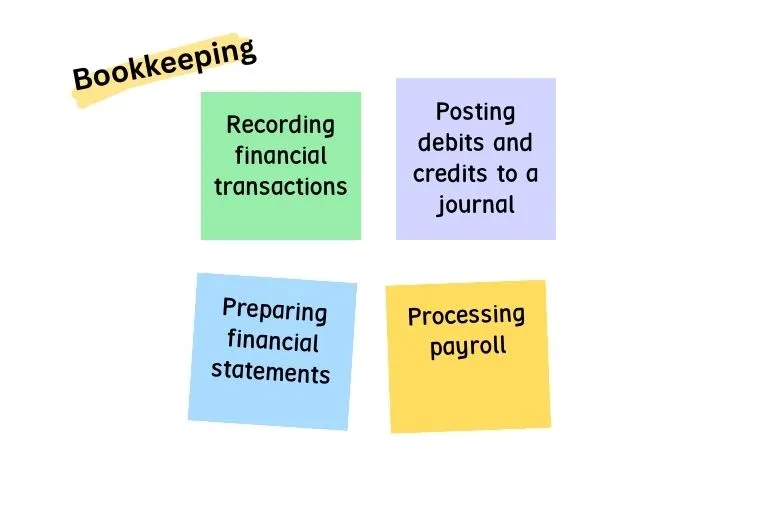
Bookkeeping focuses on the systematic recording of financial transactions. It’s the groundwork that supports broader accounting processes. Key tasks in bookkeeping include:
- Recording financial transactions
- Posting debits and credits to a journal
- Preparing financial statements
- Processing payroll
In essence, bookkeeping is all about accurately tracking the financial details on a day-to-day basis. It ensures that all data is in place for future evaluation.
Accounting: The Bigger Picture
Accounting, by contrast, takes a more comprehensive view. It utilizes the detailed records from bookkeeping to assess and interpret the business’s financial health. Typical accounting responsibilities include:
- Reviewing and analyzing financial statements
- Preparing adjusting entries
- Performing audits
- Filing relevant tax returns
While bookkeeping provides the raw data, accounting transforms it into valuable insights. Accountants use this information to advise business decisions and strategic planning.
Without accurate bookkeeping, accountants cannot perform their roles effectively, making bookkeeping an indispensable aspect of financial management.
Read more: What Is The Difference Between Bookkeeping And Accounting?
3 Key Benefits of Bookkeeping
If you’re new to the business, you might be wondering why bookkeeping is so important. Whether you outsource the work to a professional bookkeeper or handle it yourself, bookkeeping offers a range of advantages that can propel your business forward.
1. Access to Comprehensive Financial Records
Keeping meticulous records of financial transactions gives you instant access to essential financial data. For streamlined management, bookkeepers often categorize transactions, simplifying the retrieval process when needed. Typical categories include:
- Sales and Purchases
- Employee Compensation
- Tax Payments
With organized records, generating accurate reports becomes a breeze. Key reports, such as the balance sheet and income statement, offer insights into your company’s financial activities, making it easier to understand the health of your business.
2. Informed Decision-Making
Having structured financial data at your fingertips empowers you to make well-informed decisions. Financial statements like:
- Balance Sheets
- Profit and Loss Statements
- Cash Flow Statements
These documents provide a clear view of your business’s performance. They’re invaluable tools for setting achievable goals and identifying areas needing improvement. Regularly analyzing these reports allows you to spot discrepancies early, preventing potential financial pitfalls.
3. Streamlined Tax Preparation
Efficient bookkeeping simplifies the daunting task of tax filing. By maintaining up-to-date records throughout the year, you can ensure compliance with tax regulations and minimize last-minute stress. Essential documents often required for tax purposes include:
- Transaction Records
- Comprehensive Financial Reports
- Tax Compliance Documentation
A robust bookkeeping system not only aids in accurate tax reporting but also ensures that you meet all legal standards, providing peace of mind during tax season.
Read more at Recordkeeping.
2 Types of Bookkeeping for Small Businesses
When deciding on bookkeeping methods for your small business, it’s essential to understand the two primary types: single-entry and double-entry bookkeeping. Each caters to different business needs and transaction volumes, helping you manage your finances effectively.
1. Single-Entry Bookkeeping
Single-entry bookkeeping is straightforward and perfect for sole proprietors or small startups with simple financial activities. This method involves recording each transaction only once, making it easy to handle and maintain.
Here’s what you’ll need:
- Cash Sales Journal: Tracks all incoming revenue.
- Cash Disbursements Journal: Records all outgoing expenses.
- Bank Statements: Ensures that entries correspond with your bank’s records.
This uncomplicated system helps businesses monitor their cash flow efficiently, especially when transaction volumes are low and uncomplicated.
2. Double-Entry Bookkeeping
In contrast, double-entry bookkeeping is more detailed and suited for businesses with more complex financial activities. This method requires recording each transaction in two accounts, using debits and credits to maintain balanced and accurate records.
Crucial documents for this method include:
- Journal Entries
- General Ledgers
- Inventory Records
- Cashbooks
- Accounts Payable and Receivable
- Loan Documentation
- Payroll Records
Double-entry bookkeeping is essential for comprehensive financial oversight and is widely supported by many accounting software programs. It offers a robust framework for tracking financial health and ensuring transactional accuracy, making it a favorite for businesses needing detailed accounting.
Accounting software applications such as QuickBooks use a double-entry bookkeeping approach. Bookkeepers use this strategy to report transactions as expense or income, classifying them appropriately with a second entry.
Read more: Dive into our expertly crafted e-book on bookkeeping and discover the golden keys to financial mastery. Packed with invaluable insights and easy-to-implement strategies, this guide is your first step towards financial empowerment. Say goodbye to financial confusion and hello to clarity and growth.
Bookkeeping Best Practices
Now that you’ve mastered the fundamentals of bookkeeping, let’s delve deeper into how to practice proper bookkeeping. There is no one-size-fits-all solution to effective bookkeeping, but there are some general guidelines. The four bookkeeping methods listed below might assist you in staying on top of your company’s finances.
1. Adopt a Phased Implementation Approach
Transitioning from manual to digital bookkeeping? Avoid biting off more than you can chew. Opt for a phased transition instead. Implementing changes gradually allows your team to adapt to new systems without feeling overwhelmed. These careful steps enable a smooth integration process, giving everyone time to acclimate to new technologies and methodologies.
Small steps also allow you to manage your organization on a new and enhanced system effectively. This approach minimizes stress and ensures a successful transition to digital bookkeeping.
2. Maintain an Up-to-Date General Ledger
The backbone of effective bookkeeping lies in a well-maintained general ledger. This ledger collects all financial transaction records, covering both balance sheet accounts (like liabilities, equity, and assets) and income statement accounts (such as revenue and expenses).
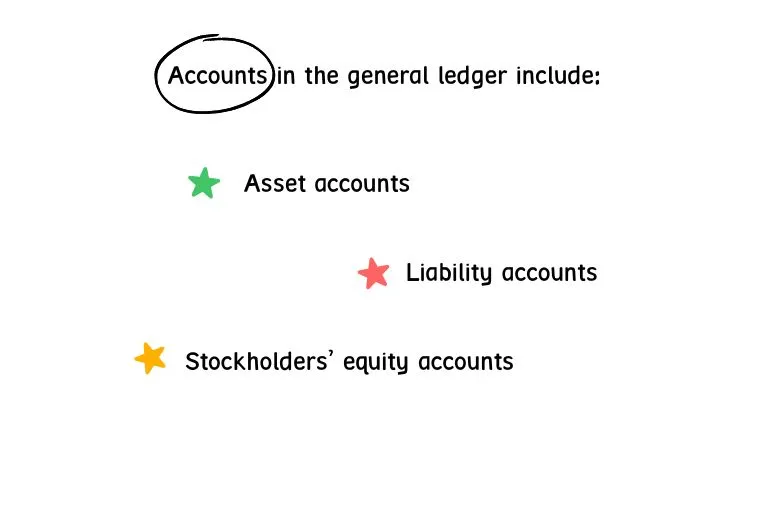 Under the double-entry accounting structure, every business transaction will affect two or more general ledger accounts. General ledger accounts include:
Under the double-entry accounting structure, every business transaction will affect two or more general ledger accounts. General ledger accounts include:
- Asset Accounts: Cash, Accounts Receivable, Investments, Land, Equipment, Inventory
- Liability Accounts: Accounts Payable, Accrued Expenses Payable, Customer Deposits, Notes Payable
- Stockholders’ Equity Accounts: Common Stock, Treasury Stock, Retained Earnings
Keeping your general ledger current helps in efficient data access and ensures smooth navigation within your bookkeeping software. QuickBooks is an excellent option for both new and experienced digital bookkeepers.
3. Separate Personal and Business Finances
Maintaining a clear distinction between personal and business finances is crucial. Mixing the two can create confusion and increase the risk of errors, potentially triggering unwanted audits. Here’s how you can achieve that:
- Use a Dedicated Business Credit Card: Always charge business expenses to a business credit card. This not only simplifies tracking but also ensures that your business expenditures are distinct from personal ones.
- Open a Separate Business Checking Account: Initiate a separate checking account exclusively for your business. This ensures that all income and expenses related to your business flow through this account, providing a clear snapshot of your business’s financial activities.
- Organize Your Receipts: Maintain distinct files for business and personal receipts. This organizational habit prevents mingling of finances and makes it easier when tax season rolls around.
By implementing these strategies, you’ll gain a clearer understanding of your business’s financial health while minimizing the chance of mistakenly misrepresenting your business’s finances.
4. Proactive Tax Planning
Efficient tax planning is essential for a smooth tax season. By maintaining up-to-date records throughout the year and staying in close contact with your tax advisor, you can ensure compliance with tax regulations and minimize last-minute stress.
- Maintain Financial Records: Regularly update your books and communicate with your tax expert to stay prepared.
- Plan for Tax Payments: Understand your tax obligations and set aside necessary funds to cover them without impacting day-to-day operations.
- Maximize Deductions: Keep detailed records to take full advantage of all possible deductions, potentially saving significant amounts on your tax bill.
Breaking the task of tax preparation into manageable, year-long processes not only keeps you compliant but empowers your business to thrive with fewer financial surprises.
Should I Do My Own Bookkeeping? 2 Questions to Ask Yourself First
Deciding whether to handle your own bookkeeping or hire a professional is crucial. It involves weighing several factors that can significantly impact your business. Here are the key questions to consider:
1. Do I Have the Expertise?
Evaluate your personal expertise in accounting and bookkeeping. A few academic courses or basic familiarity might not suffice when dealing with more complex financial records or compliance with tax laws.
- Do you have a solid grasp of accounting principles and practices?
- Are you familiar with local and federal tax regulations?
- Can you accurately manage financial records without errors?
If you possess an advanced understanding of these areas, you might be equipped to handle bookkeeping yourself. However, lacking expertise may mean it’s wise to bring in a professional to avoid financial inaccuracies.
2. Do I Have the Time?
Bookkeeping is time-consuming and requires regular attention to ensure accuracy and timeliness in financial reporting.
- Do you have the bandwidth to dedicate hours each week to bookkeeping?
- Can you maintain consistency in updating your financial records?
If managing your books feels like one too many tasks on your to-do list, outsourcing to a specialized service may free your time for business growth and strategy.
Ultimately, choosing whether to manage your bookkeeping or outsource it boils down to these core considerations. Being realistic about your skills and schedule can prevent costly mistakes and help you focus on what truly matters: growing your business.
Ready to Get Started?
With the assistance of a licensed professional, you can cross routine bookkeeping off your never-ending to-do list. Contact XOATAX to connect with a live bookkeeper who can help ensure that your company’s books close on time each month and that you’re ready for tax season. Our CPAs and Tax Experts have an average of 15 years of experience working with small businesses in a variety of industries.
Whether you’re looking for the best accounting system for your company, learning how to interpret a cash flow statement, or creating a chart of accounts, XOATAX can help.



 anywhere
anywhere  anytime
anytime