For Nonresident Aliens living in the United States, filing form 1040NR is essential. Navigating the maze of deductions a nonresident alien can take on this tax form can be confusing and overwhelming. For this reason, many nonresidents need to understand clearly the Form 1040NR instructions and how to file it.
With careful attention to detail and strategic deduction, you can make filing much easier and less stressful.
Key Takeaways
- Form 1040NR is the federal income tax form for nonresidents and foreign individuals that must file by the due date each year to avoid IRS fines or penalties.
- US citizens who don’t have a green card or meet the IRS’s substantial presence test in any given tax year will be considered nonresidents for taxation purposes.
- They must file their returns – Form 1040NR or 1040NR-EZ – by June 15th of the following year.
- As an employee who received wages subject to U.S. income tax withholding, you must file your Form 1040NR by April 15th day of the following year. If you cannot file your return by the due date, you can file Form 4868 for an automatic 6-month extension.
What Is Form 1040-NR: U.S. Nonresident Alien Income Tax Return?
For tax purposes, nonresidents of the United States must complete Form 1040-NR: U.S. Nonresident Alien Income Tax Return.
Nonresident Alien must file Form 1040-NR to report income earned from U.S. sources such as wages, interest and dividends, capital gains, pensions other source income sourced from American countries or territories.
Additionally, the form provides information on any allowable deductions or credits to help reduce your tax liability to comply with US taxation laws.
>>Related post:
- Form 1040: A Step-By-Step Guide To Gain Income Tax Return
- Form 1040: Choosing Appropriate Schedules And Types
Get All the Potential Savings by Filling Out Form 1040NR Correctly
With tight filing deadlines around the corner, it’s vital to be mindful of potential difficulties or complexities when preparing your taxes. From following our instructions to maximize any potential savings with form 1040NR successfully:
Filing Status Section
It all starts with the filing status of Form 1040NR. When completing this document, individuals must make an important choice: select “Resident Alien” if they are considered a resident of the United States or choose “Nonresident Alien” when applicable for non-residents.
Other available filing statuses apply in certain circumstances, such as Dual-Status Aliens, Married Filing Separately, or Not Liable for U.S. Tax. Selecting the correct filing status is critical to ensure accurate filing, benefitting from potential refunds, or avoid excessive tax liabilities.
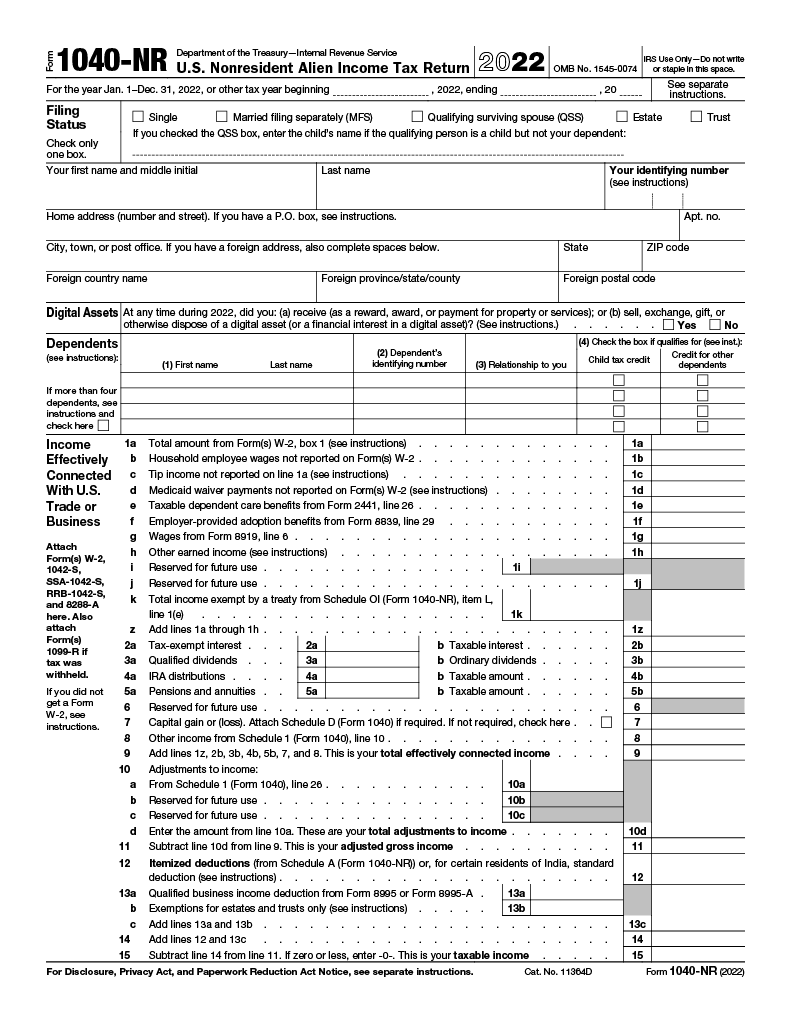
Income Effectively Connected With U.S. Trade or Business
Determining the appropriate filing status is the first step in ensuring a triumphant return. Afterward, thoroughly review all income sources listed from Links 1a-15 on Schedule NEC for accuracy.
Links 1a through 15 of Schedule NEC include dividends, dividend equivalents, interest, royalties, pensions, annuities, and other income forms that may be tax-subject.
Depending on the particular circumstances, different types of income will be taxed at a different rate or may be eligible for reduced rates or exemptions under a tax treaty.
If the tax rate is 30%, 15%, or 10%, you should take advantage of columns (a) through (c). In cases where the rates do not apply, you should use column (d) instead.
Tax and Credits
After looking into income sources and their related forms, you’re now ready to explore Taxes and Credits.
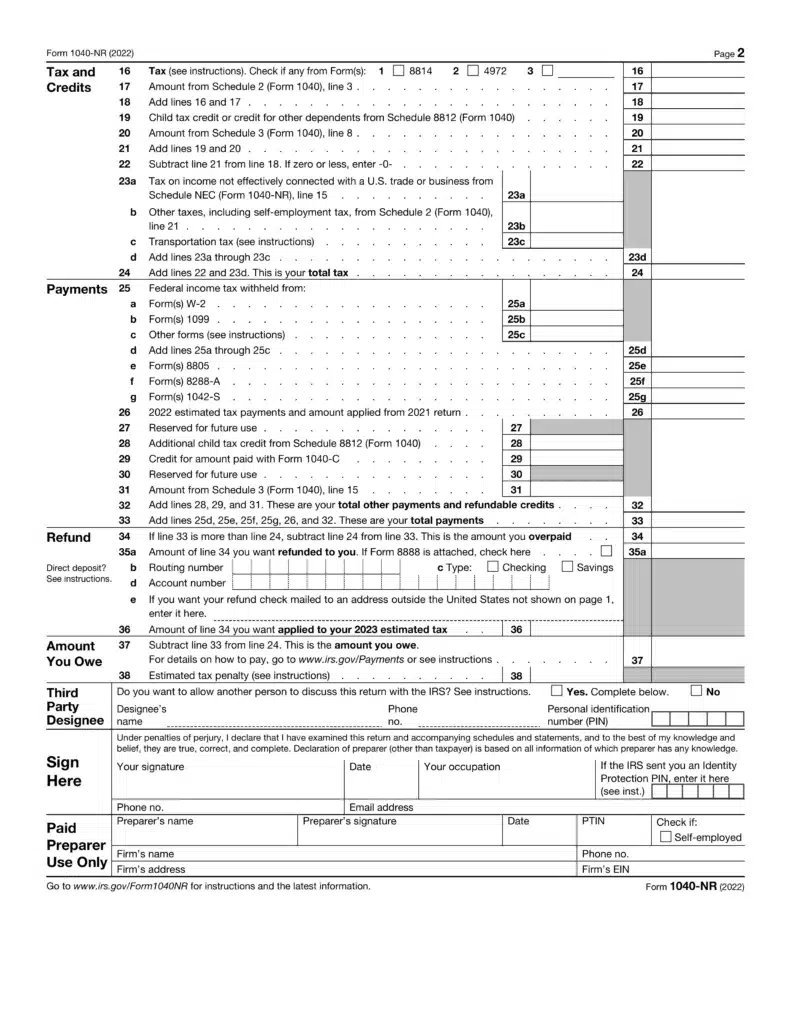
Line 16 of Form 1040NR reports the total tax liability due. Exceptions must be considered, including Tax Rate Schedule W for estates/trusts and omitting certain items.
Furthermore, the Foreign Earned Income Tax Worksheet and Form 8615 may apply depending on specific criteria. Lastly, calculate your tax due accurately by referring to the Schedule D Tax Worksheet and Qualified Dividends and Capital Gain Tax Worksheet in the Instructions for Form 1040.
Taxpayers can claim certain credits, such as the Earned Income and Child Tax Credit (line 19), if they meet eligibility requirements.
Line 17: report the total amount from Schedule 2, line 3. This amount reflects an individual’s adjusted gross income following certain deductions and credits
Line 20: report the total amount from Schedule 3, line 8. This amount reflects any foreign taxes an individual owes in addition to domestic tax liabilities. You must accurately calculate and report these amounts to pay all their due taxes and credits adequately.
Payments
After you’ve reviewed the applicable deduction, credits, and exemptions from the Tax and Credits section of Form 1040-NR, you can now proceed to Payments.
Line 26 of Form 1040-NR covers estimated tax payments for 2021. Taxpayers should substitute their ITIN or Social Security Number wherever the instructions mention.
However, line 27, reserved for future use, should remain blank, and individuals filing this form cannot claim the earned income credit (EIC).
Line 28 of Form 1040-NR allows for the refundable child tax credit or additional child tax credit for nonresident aliens with a principal place of abode in the U.S. for more than half of 2021. Eligibility may apply to those with “J” and “Q” visas.
Line 29 of Form 1040-NR covers the credit for the amount paid with Form 1040-C, which you can enter on line 29. Those filing this form cannot claim the American Opportunity Credit.
Refund
After carefully considering the Payments section of Form 1040-NR, you are likely eligible to receive a refund. Line 34 of the form shows the amount overpaid. Lines 35a through 35d provide information about what to report to receive a refund.
If you have requested a refund of tax withheld on certain forms such as 1042-S, 8805, or 8288-A, allow up to six months for processing time. For overseas addresses, enter the address on line 35e of the form.
Amount You Owe
After understanding your potential refund amount, reviewing line 34 to determine the amount overpaid in taxes, penalties, and interest is crucial.
If you owe taxes, you must pay the total amount to avoid any further action by the IRS. Paying this balance entirely is the only way to prevent additional penalties or interest from accruing. You can make payments using a check, money order, or electronic fund transfer.
Additionally, the estimated tax penalty may apply if the amount of tax you owe is more than what you paid throughout the year. This penalty relies on completing Line 38 of Form 1040-NR; a completed form must accurately calculate current and prior year taxes.
You can avoid the estimated tax penalty if you have paid at least 90% of your current year’s taxes or 100% of the taxes due for the prior year. When paying estimated tax penalties, an electronic fund withdrawal or check made out to the “United States Treasury” is required.
Filing your taxes doesn’t have to be a stressful ordeal. With the correct information and an understanding of your Form 1040-NR obligations via clear instructions, you can confidently complete all necessary reporting and get the best possible outcome for your finances.
Let’s wrap up this discussion on confidently meeting your Form 1040-NR tax requirements!
Who Will Be a Non-Resident Alien?
- This category includes those with a temporary visa, such as students or workers, and those who stay in the U.S. for fewer than 183 days during the tax year.
- When determining whether an individual is a non-resident alien, one should consider their immigration status, length and type of stay in the U.S., and other applicable regulations.
- If you do not obtain a green card or meet the substantial presence test in a given tax year, you will be a non-resident alien for tax purposes.
Green Card Test
Individuals must not have a green card to be deemed nonresident aliens. The Green Card Test determines if an individual is a US resident for tax purposes. To meet the criteria, one must be a legitimate permanent inhabitant of the United States in any given calendar year.
US Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) issues green cards to nonresidents of the United States. This allows you to live and work permanently in the U.S. This evaluation gives lawful US residents a chance to be considered tax-paying citizens regardless of nationality.
As a result, it helps to differentiate between permanent and non-permanent resident aliens for tax purposes. This test is essential to understanding how one’s tax filing status may be affected.

Substantial Presence Test
This helps to provide a more precise determination of an individual’s residency status for tax purposes.
It is a more comprehensive way of evaluating an individual’s residency status for taxation purposes. This test examines the number of days an individual has been physically present in the United States in 3 years.
Meeting the minimum threshold of this test deems an individual a US resident for tax purposes, regardless of whether they fulfill the Green Card Test requirements.
Additionally, it helps to ensure that individuals who spend significant amounts of time in the US are accurately classified as residents when filing. If you do not meet both tests, you must file a Form 1040NR with detailed instructions.
Who Needs To File Form 1040-NR?
In case of a qualifying outcome for either of these tests, you must file Form 1040-NR to correctly fulfill your U.S. tax obligations. Individuals who need to file Form 1040-NR, U.S. Nonresident Alien Income Tax Return, include:
- Nonresident alien engaged in a trade or business in the United States during the year (even if you have no income from that trade or business)
- Nonresident alien not involved in work or business in the United States during the year has generated revenue from U.S. sources that appears on Schedule NEC lines 1 through 12
- Schedule NEC reports particular income such as Dividends and dividend equivalents, Interest, and Industrial royalties…
- Those who owe special taxes such as the alternative minimum tax (AMT) or household employment taxes
- Those who received distributions from health savings accounts (HSAs), Archer medical savings accounts (MSAs), or Medicare Advantage MSAs
- Self-employed individuals with net earnings of at least $400 in countries with which the U.S. has Social Security agreements.
- Personal representatives of deceased persons who would have had the requirement to file this form can take advantage of this evaluation.
- Represented an estate or trust that had to file Form 1040NR

When Is Form 1040NR Due? – Don’t Miss the Deadline
Time is of the essence when filing taxes as a nonresident alien. Don’t miss important deadlines when filing your form 1040NR, as this will ensure accurate and timely tax returns:
- Non-resident alien employees must file Form 1040NR by April 15th (4.5 months following the tax year).
- Foreign persons with income other than wages subject to withholding have until June 15th (6.5 months following the tax year) to file their taxes or request an extension on Form 4868.
- If you did not receive wages as an employee subject to U.S. income tax withholding, you could file Form 1040-NR by the 15th day of the 6th month after your tax year ends.
- Taxpayers granted an extension can submit their returns without paying any late filing penalties until October 15th of the subsequent year.
Be on time – with the correct information, meet your tax deadlines. Get organized and make sure your file is right on time. Mastering the instructions below will help you with avoiding penalties.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is there a standard deduction for 1040NR?
No, there is a standard deduction available for US residents. The standard deduction for 2022 is $12,950 for single filers and $25,900 for married filing jointly, and $19,400 for heads of household.
Can you electronically file form 1040NR?
You can use the IRS e-file to file your Form 1040NR electronically. Ensure you have all your tax information ready and adhere to the filing guidelines.
Do I have to file a 1040NR?
Your tax situation depends on whether you have to file a 1040NR. Generally, if you are a nonresident alien with income from U.S. sources, then you must file 1040NR. However, there can be exceptions depending on the type of income and other factors, so it’s best to talk to a tax specialist for advice before filing.







































































































 anywhere
anywhere  anytime
anytime